With the innovative ideas of electronic hardware, how to realize the concept into a physical product could be pretty challenging for startups, who have little experience in manufacturing and limited resources. We understand the difficulties and would like to provide the support to facilitate the startups at each phase of electronics manufacturing process. We would like to show you the tips and explanation of hardware development and manufacturing in a series of articles.
No matter which manufacturing stage you are at, to get the proper quotation for your product, RFQ package preparation is critical. RFQ definitely plays an essential role to communicate with the suppliers and explain what you expect your product will be.
First of all, we would like to explain the key elements to help you understand how to prepare good RFQs. In the first part, the 5 key elements related to product design will be introduced:
1. Request For Information
2. Product Description
3. Industrial and Mechanical Design
4. Electrical Design
5. Testing Requirement
What is RFQ?
Let’s start with the definition of RFQ. RFQ stands for Request For Quotation, which is a standard business process to invite suppliers into a bidding process to bid on specific products or services. For the hardware startups whose product is ready to manufacture, preparing RFQ documents for sourcing vendors is the essential step to get proper quotations from electronics manufacturing suppliers. Meanwhile, for the suppliers who are interested in providing electronics manufacturing services, RFQ helps them fully understand the buyer’s (i.e. hardware startup’s) product and service expectation. Good RFQ contains the information of specified specification of each part and help suppliers to provide quotation accurately and efficiently. Additionally, RFQs can be the legal binding documentation for suppliers and help buyers reduce internal and external communication cost.
Lets’ start the RFQ package preparation.
1. Get Your RFI Ready Before RFQ
Before RFQ, RFI (Request for Information) is the step you should not skip to gather information and help make decisions for the next steps. RFI is a standard business process used by buyers to collect written information regarding the capabilities of various suppliers, which will better inform buying decisions. Generally speaking, the buyers need to provide the information, including user scenario, market research, and product concept. In addition, the general spec should be prepared as well, such as electrical spec, mechanical spec, schedule, new feature implementation plan, etc. If you are not sure whether the specs could be prepared by your internal resources, contacting experienced product managers for consultancy would be helpful. We could help hardware startups to find the electrical/mechanical solutions and guide you through the process of RFI and RFQ.
The more information you share, the more trust and help you can expect from the electronics manufacturers. Suppliers can be your partners as well. In this sense, you will like to get the good quality manufacturers to be interested in your project, and you should treat those potential manufacturers as your investors. Regard the manufacturer as one of your investors and show them your investor deck, including
- Product differentiation
Describe the difference/advantage of the product or service comparing to competitors.
- Market outlook
Share the market research and your target market segmentation.
- Traction/sales
List the sales channels and the countries where you will be selling the product and also provide any business models.
2. Describe Your Product
After collecting the supplier information, now you have a clearer roadmap for your product and want to get the best price for your project from qualified electronics manufacturing suppliers. Describing your product with documents is the first step to begin RFQ package preparation. The documents, such as design concept, specification, and features, should be defined and prepared.
- Design Concept:
Design concept consists of two parts: textual and visual. For textual part, you will describe a specific issue that your product tries to solve. For visual part, you will describe the image and color of the product. In this section, you also need to provide some examples to describe the use cases and user scenarios of the product.
Take Angee, the smart home security device, for example:
Angee’s most important function is fully-automated smart security to protect your home and family. With voice recognition, at-the-door identification, and a portable 360° rotating camera—all without any subscription fees—Angee is revolutionizing home security. It’s voice-controlled and integrates with your other smart home devices and favorite apps. It has two-way audio and streaming video so you can keep in touch from anyway in the world.
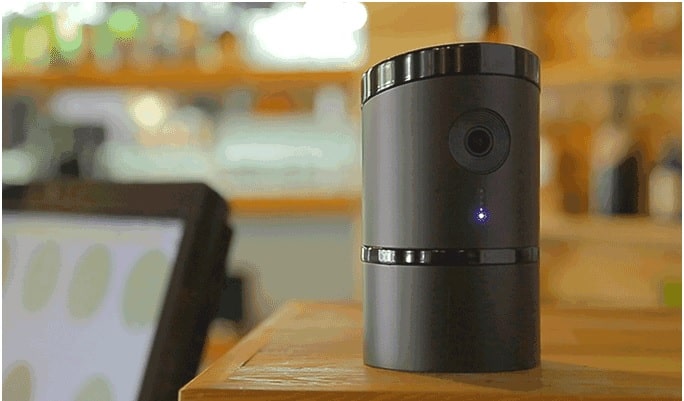

Features
All the functions of your product should be listed clearly, which helps manufacturers understand how you expect your product works.
For example: Angee
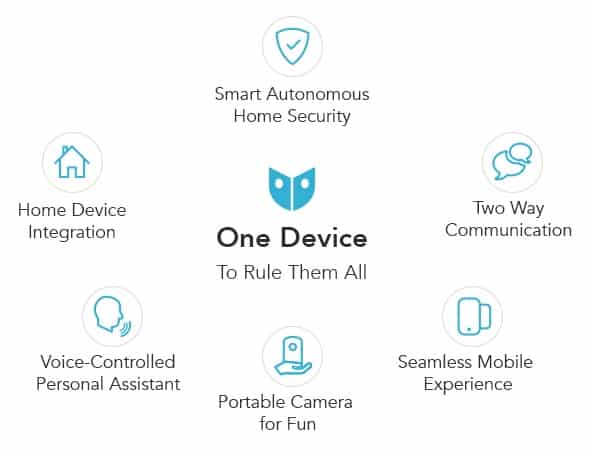
Specification (electrical and mechanical)
To describe your product in detail and help manufacturers understand what you would like your products to be, you need to provide electrical specification and mechanical specification.ProcessorARM Cortex-A9
Wireless connectivityWireless connectivity:Camera sensorCMOS Full HD (1080p), Active resolution: 1920x1080Video encodersHigh-performance h.264 encoder capable of 1080p@30 fps, Real-time stream over wi-fiMotion detection6x passive infrared sensor (PIR), Covering area 360 degrees around the deviceBattery operationBuilt-in rechargeable Li-lon (3600 mAh), Streaming time up to 10 hoursSecurity Tag2x alkaline AAA battery, Bluetooth 4.1, Accelerometer and gyroscope
3. Industrial & Mechanical Design
To define the shape and every part of the product, clear and precise industrial and mechanical design is critical. Even you modify the length of your product for 1 cm, it may affect the quotation. The dimension and shape of your product and how the product should be assembled should be described accurately in the following files. In general, the 2D files and 3D CAD files could be generated by AUTOCAD or AUTODESK Fusion 360. If you are still not sure what should be included in the files, we can provide professional consultation to help with the mechanical design.
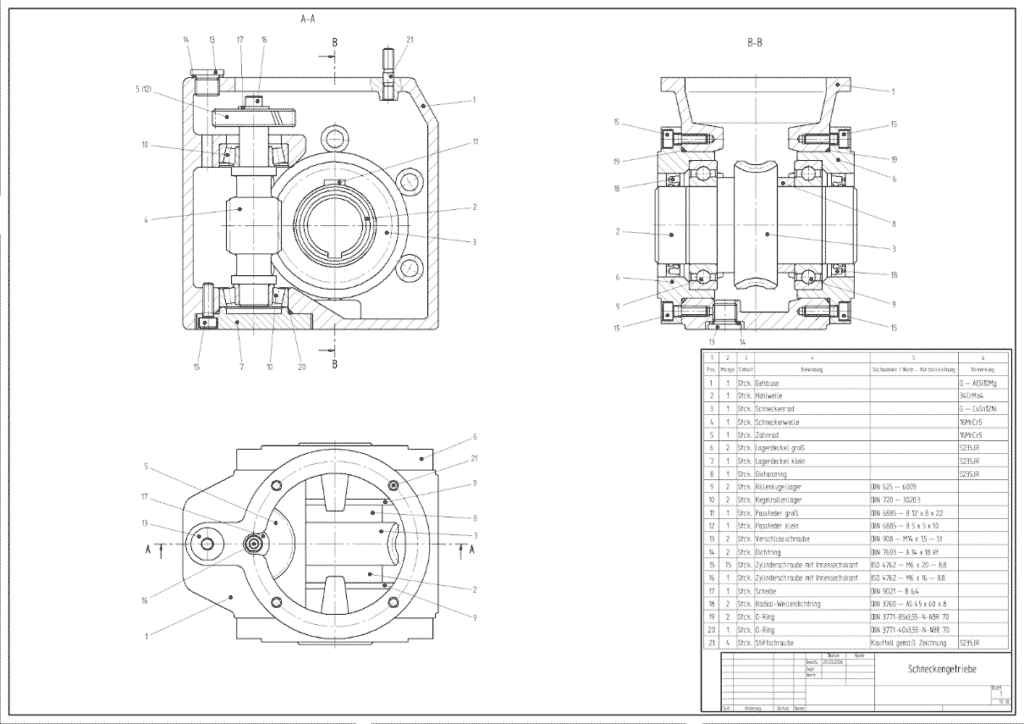
2D File2D file is used for manufacturers to understand the dimensions of the industrial design.
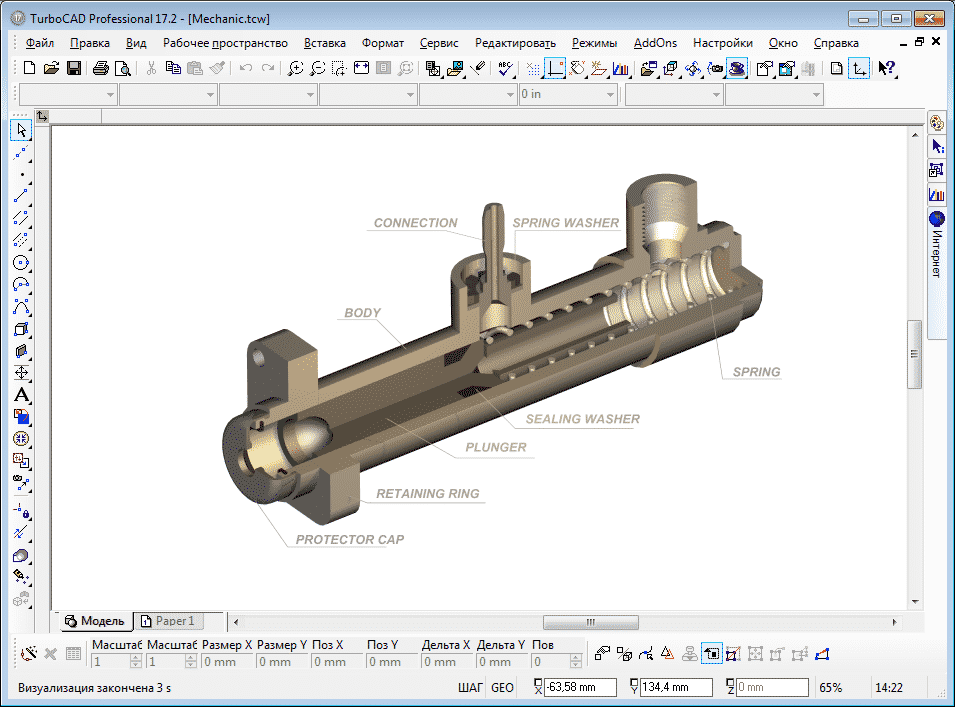
3D CAD File
3D CAD files are the design files for the manufacturers to understand the shape in 3 dimensional. The material and color of each mechanical part can be listed in the file as well.
- Assembly SOP Document
Most of times, buyers leave assembly SOP to the manufacturer to design because manufacturers have the expertise to set the production line in the most efficient way for the product. However, you will need to understand the assembly SOP as well because extra work station in the production line would cost you extra. Here, of course, you can consult with us for the support to prepare assembly SOP document and negotiate with suppliers about the execution on production lines.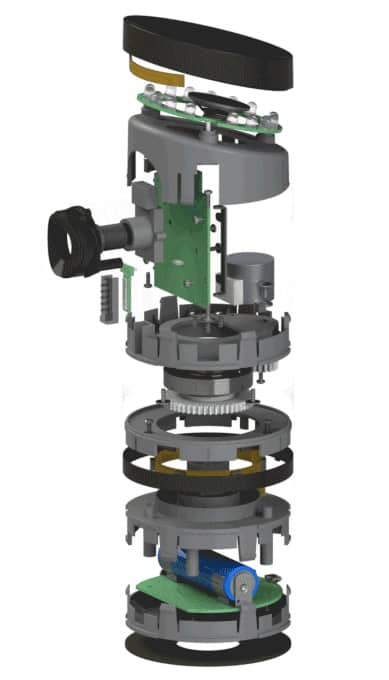
- Special Manufacturing Process
This section contains the additional information that requires the manufacturers to pay attention for the special requirements while manufacturing the product. You might have collected the information in the RFI stage. Here we listed some examples for the manufacturing process. If you are still not sure what process you will need, we can provide the consultation to help you to find the items you may need.
4. Electrical Design
Electrical design is like the brain of your electronics product. To make the product function successfully, you need to list: what components you will use, how the wires and chips are connected, what kind of PCB you need. At the stage, you will need to prepare 3 types of document: BOM (Bill of Materials), Schematics, and Layout (Gerber file).
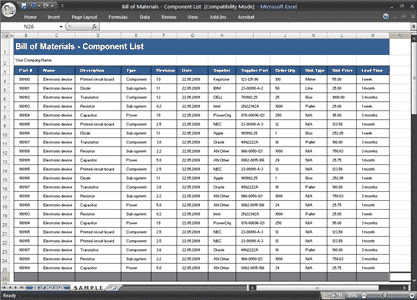
1. BOM
The BOM is essentially a comprehensive list of electrical parts that the product uses. At the RFI stage, you might have surveyed all the components and electrical parts. So now at RFQ stage, the buyers need to provide BOM to get accurate quotation from suppliers. If some components require special process, please mark them. For example, some of wireless chips/modules need pre-baking before the pilot run.
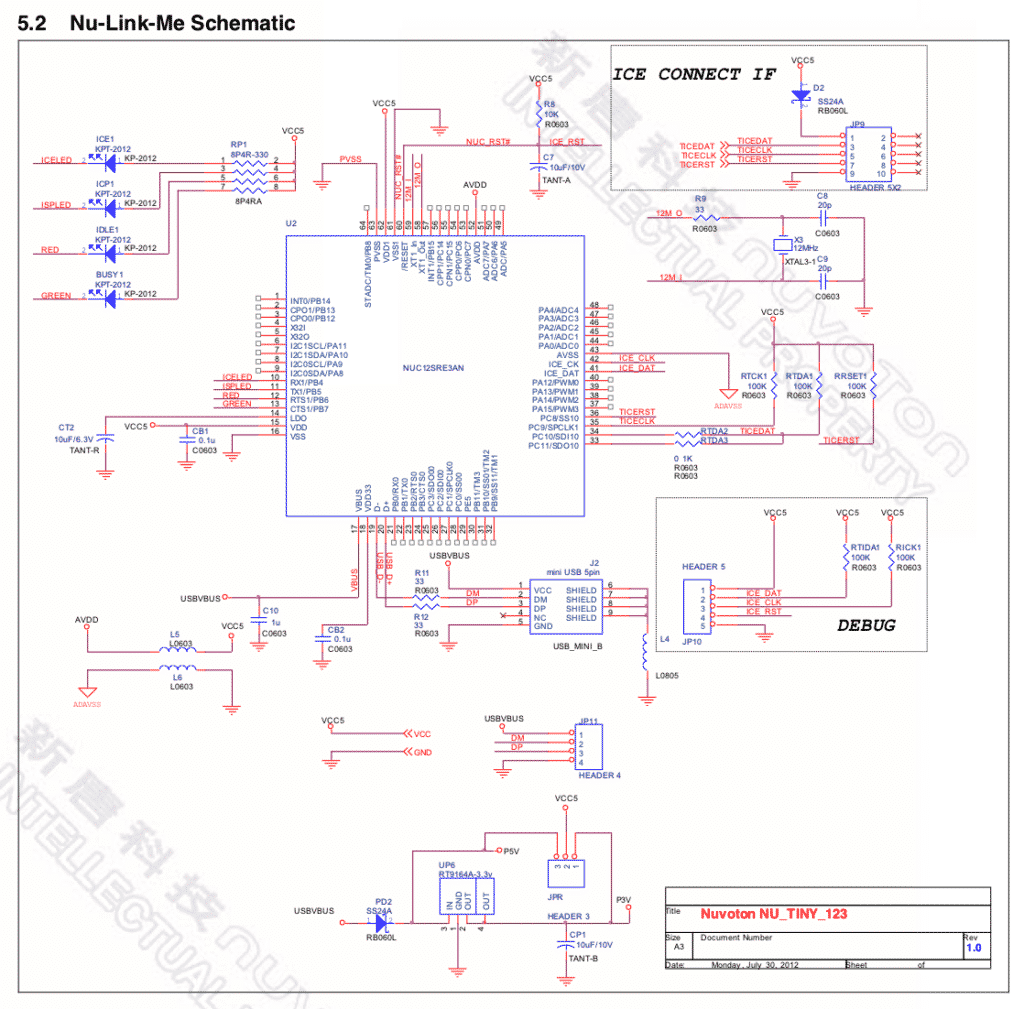
2. Schematics
Schematics use symbols for each component in an electrical circuit to show the electrical interconnections between the components. In the diagram, the schematics do not show placement or scale but function and flow only.
3. Layout/Gerber file
To present the location/placement of each part on the PCB and also show how each trace connects to each component in different PCB layers. PCB stands for Printed Circuit Board, which is a key fundamental element for the electrical design. There are several factors that could affect the quotation of this part: dimensions, layers, thickness, copper weight, coating, color and test, etc.
For example of layout: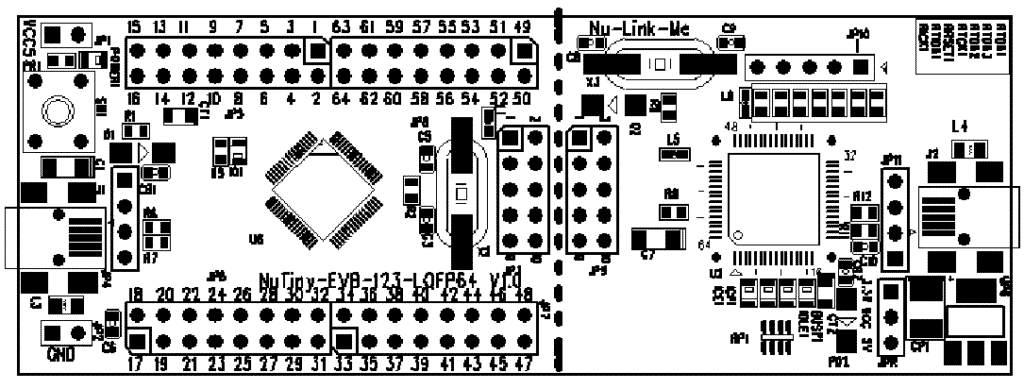
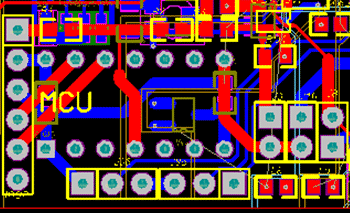
In TechDesign, we have a list of suppliers that can help you to design the PCBA and manufacture in a small batch run.
5. Testing Requirements
To make sure your product functions correctly and meets your expectation, defining the testing requirements clearly is an indispensable process in working with manufacturers. Here are the factors you need to consider:
| Category | Objectives |
|---|---|
| Environment | |
| Operating temperature | To see if the product can be fully functional in the operating temperature range |
| Humidity | To see if the product can be fully functional within the specified humidity range. |
| ESD (electrostatic discharge) | To see if the product can be operated when injecting different amount of ESD to the product |
| Thermal | To understand the max and min temperature that the product will fail to operate. |
| Transportation | |
| Vibration | To see if the product can handle the vibration during the transportation |
| Drop | To see if the product can handle the drop in different levels of height. |
| High and low temperature storage test | To see if the product still can fully operate after the extreme storage temperature |
| Product Life Cycle | |
| Open/Close | To verify the hinge of the product (open and then close for 100000 times) |
| Connector | To verify the connector of the product (Plug in, plug out for 100000 times) |
| Button | To verify the button (keep pushing the button for 100000 times) |
| Burn-in (Full function) | To verify the full capacity of the product for certain number of hours. For example, 168 hours for tablet. |
| Mechanical | |
| Shock | To verify if the product is stable enough when providing the outside force to impact the product. |
| System bending | To verify the max stress of partial parts or the whole product when bending |
| Equipment Assurance | |
| Audio quality | To verify the quality of the sound from the audio |
| GPS/ Glonass | To verify the accurateness of the GPS |
| LCD screen | To verify the LCD panel |
Conclusion
We have introduced the key elements you would need while sourcing electronics manufacturers. Hope this information is helpful for you to prepare RFQ packages. The next step is to share your business information with the potential vendors. For most suppliers, the quantity of the order and the potential of product could be one of the concerns to decide whether to provide the electronics manufacturing services and how many components they should prepare in advance. In the next article, “Request for Quotation (RFQ): Sourcing Electronics Manufacturers—Part 2 Business” will show you 4 more things you need to think about while sourcing the appropriate vendors.